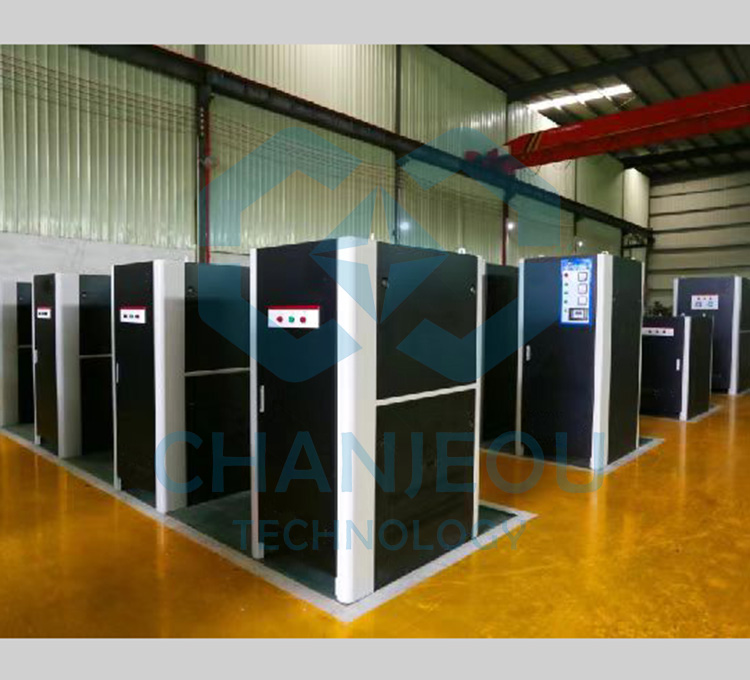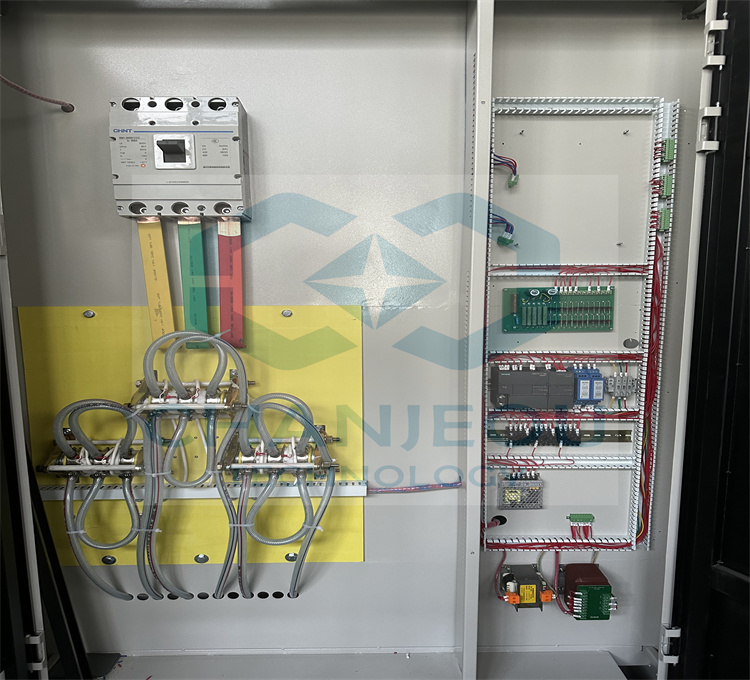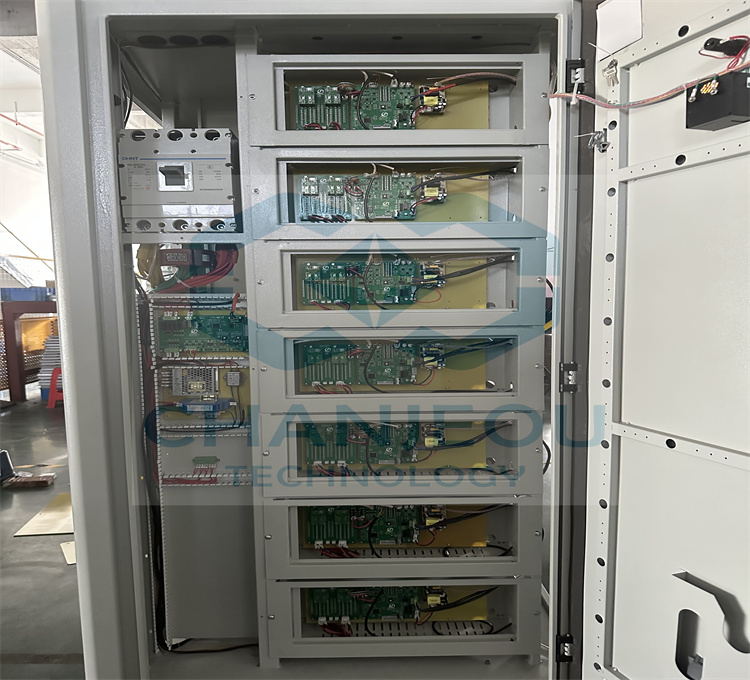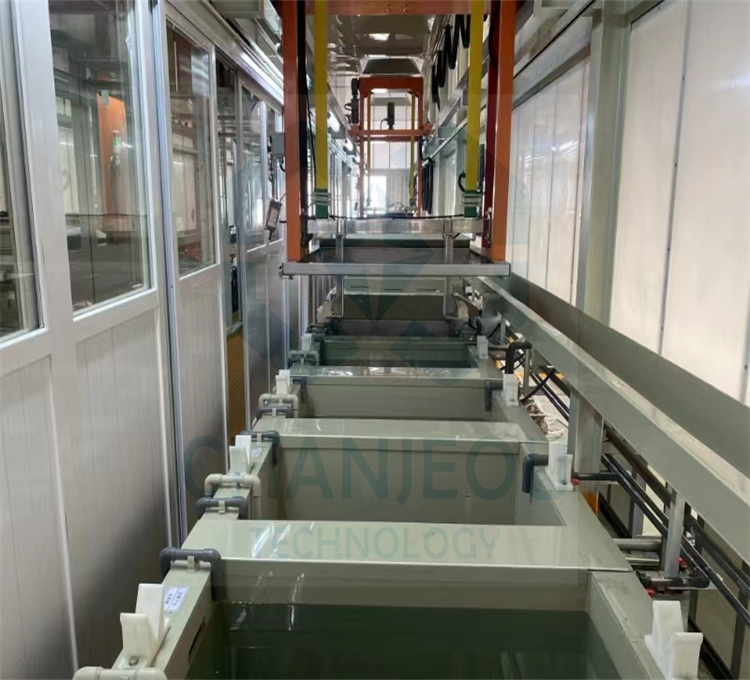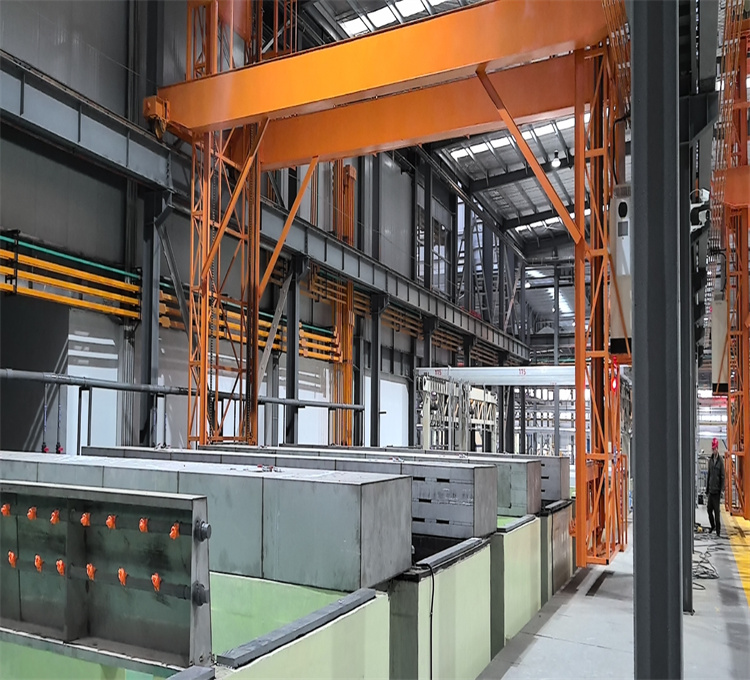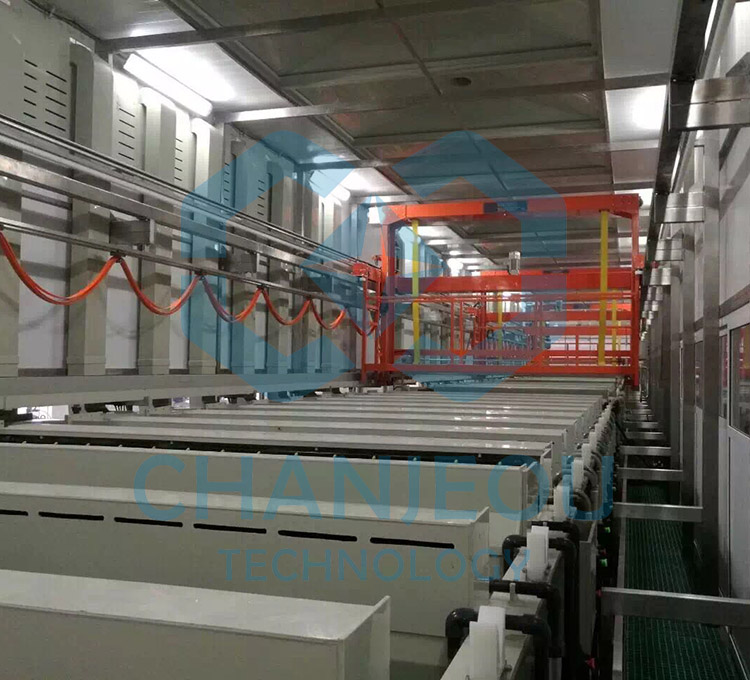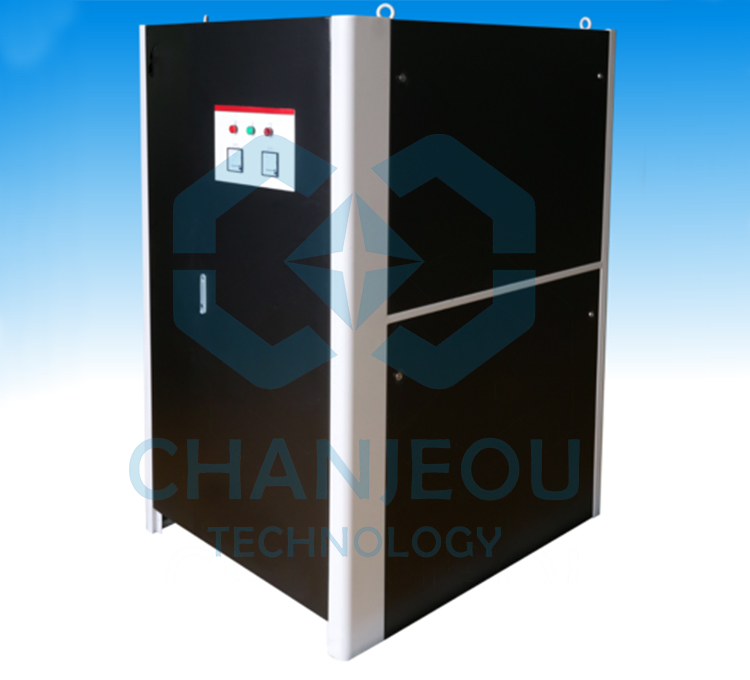
Fonte de alimentação de oxidação do retificador de anodização de alumínio IGBT
Três tipos de fonte de alimentação de oxidação do retificador de anodização de alumínio:
1, IGBT de economia de energia de alta frequência
2, SCR tipo controlado por silício
3, tipo regular de alta frequência
Três tipos de retificador de anodização de alumínio (fonte de alimentação de anodização):
1, retificador de fonte de alimentação de anodização de economia de energia de alta frequência - terceira geração
2, Retificador de fonte de alimentação de anodização de alta frequência regular - segunda geração
3, Retificador de fonte de alimentação de anodização controlada por silício -- primeira geração
Contraste de eficiência do retificador de fonte de alimentação de anodização:
| Nome | Tipo controlado por silício | tipo regular de alta frequência | tipo de alta frequência de economia de energia |
| Eficiência do retificador | 80%~86% | 88%~90% | 82~95% |
Análise de economia de energia para três tipos de fonte de alimentação de oxidação anodizante (retificador de anodização):
| Tipo controlado por silício | Tipo regular de alta frequência | tipo de economia de energia de alta frequência | |
| capacidade de potência | 15KA/22V | 15KA/22V | 15KA/22V |
| eficiência nominal | 86% | 91% | 95% |
| Saída típica | 15KA/16V | 15KA/16V | 15KA/16V |
| Eficiência de uso típica | 83% | 88% | 94% |
| potência de saída CC típica | 289,1 | 272,7 | 255,3 |
| consumo de eletricidade em uma hora | 289,1 | 272,7 | 255,3 |
| consumo de eletricidade em um ano (4320 horas) | 1248912 | 1178064 | 1102896 |
| custo unitário de eletricidade | 0,9 RMB | 0,9 RMB | 0,9 RMB |
| Custo de eletricidade de um ano para um conjunto | 1124020 | 1060257.6 | 992606 |
| Compare com o tipo controlado por silício, economia de energia | 63762.4 | 131413.6 | |
| comparar com o tipo regular de alta frequência | 67651.6 | ||
| Resultado | O retificador de anodização de alta frequência com economia de energia ajuda o cliente a economizar muito custo | ||
Dados técnicos do retificador de anodização de alta frequência para economia de energia:
| tensão de entrada CA | 380 V, 50 Hz (personalizado) |
| tensão de saída CC nominal | 8~60V (personalizado) |
| corrente de saída CC nominal | 1000~30000A (personalizado) |
| faixa ajustável de saída | 5%~100% nominal contínuo ajustável |
| saída precisão estável | menos de +-0,2% |
| suave para cima suave para baixo ajustável | Sim |
| definir limite de corrente, limite de tensão, falta de fase de tensão, proteção contra superaquecimento, proteção contra falta de água, etc. | Sim |
| Fixação de tensão de operação (CV), Fixação de transferência de corrente de operação (CC) | Sim |
| Método de resfriamento | resfriamento a água ou a ar |
Atualmente, os retificadores de oxidação mais usados são IGBT e SCR, cujas diferenças são as seguintes:
O sistema de controle IGBT é mais complicado que o SCR, se alguma coisa precisar de manutenção, é um pouco difícil para o cliente manusear, então normalmente sugerimos o retificador SCR:
Painel de controle do retificador de anodização SCR
Painel de controle do retificador de anodização IGBT |
| ambos os retificadores SCR e IGBT podem usar resfriamento a água ou a ar |
| ambos os retificadores SCR e IGBT podem ser com filtro harmônico |
| O retificador de oxidação IGBT pode economizar 6% de eletricidade |
| O preço do retificador IGBT é menor que o do retificador de anodização SCR |
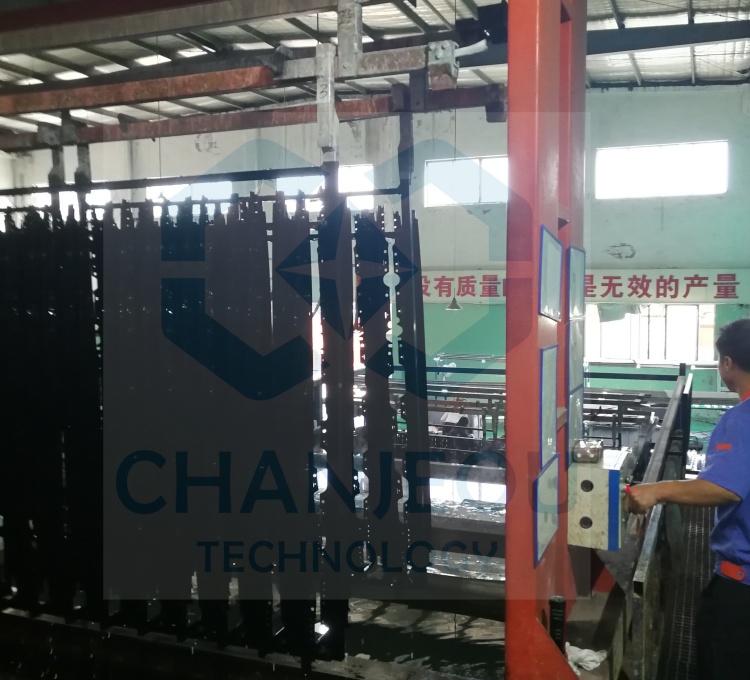
Foto do local de fabricação do retificador de anodização:
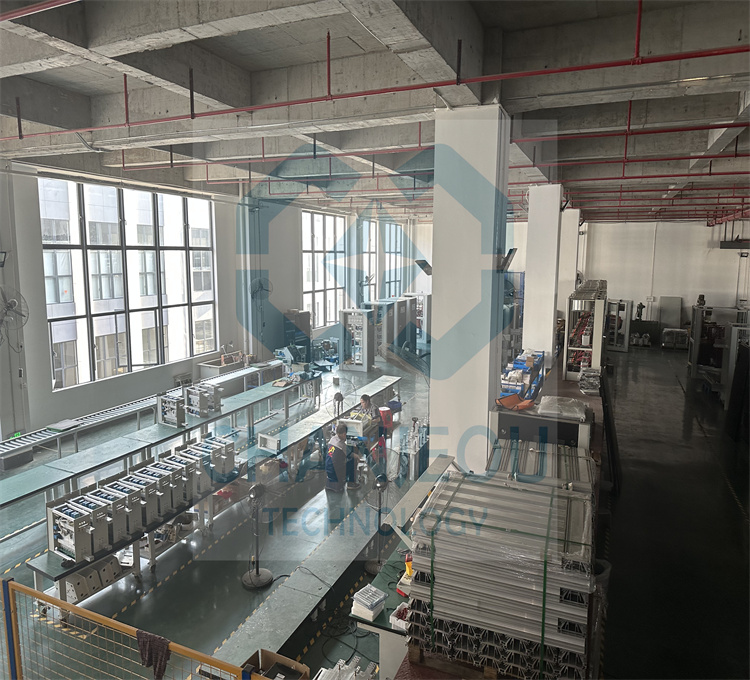
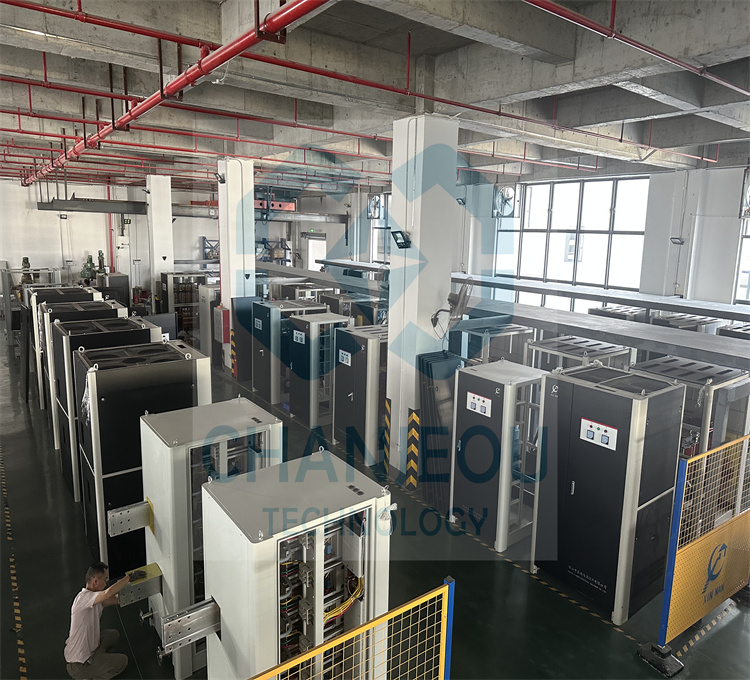
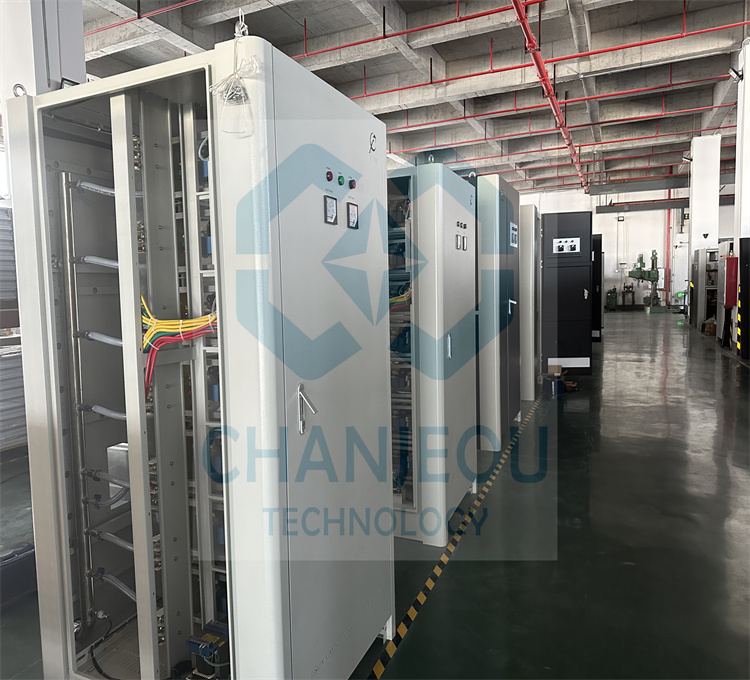




Falhas comuns e métodos de solução de problemas de oxidação de fonte de alimentação de alta frequência (retificador IGBT)
1、 Falha de sobrecarga
Quando a fonte de alimentação de alta frequência de oxidação estiver em operação, se os aparelhos elétricos excederem a carga nominal da fonte de alimentação, ocorrerão falhas de sobrecarga. Neste ponto, a energia será desligada automaticamente para proteger os componentes eletrônicos internos, evitando assim curtos-circuitos e danos causados por sobrecarga. Para resolver a falha de sobrecarga, as seguintes etapas podem ser tomadas para solução de problemas:
1. Verifique se os aparelhos elétricos estão sobrecarregados e, em caso positivo, substitua-os por aparelhos que atendam às especificações;
2. Determine se a carga nominal da fonte de alimentação está correta. Se estiver incorreta, substitua-a por uma fonte de alimentação que atenda aos requisitos;
3. Verifique se a fonte de alimentação está instalada corretamente. Se houver alguma anormalidade, a fonte de alimentação precisa ser reinstalada.
2、 Falha de curto-circuito
Se a fonte de alimentação de alta frequência de oxidação encontrar um curto-circuito durante a operação, ela parará de funcionar imediatamente. Isso ocorre porque a fonte de alimentação descobriu que a carga do circuito estava muito alta e a corrente excedeu o valor nominal, resultando em um curto-circuito no circuito. Para resolver a falha de curto-circuito, você pode tentar os seguintes métodos:
1. Verifique se as conexões do circuito estão soltas e, se necessário, reconecte-as;
2. Verifique se há objetos estranhos no ambiente de trabalho e remova-os se necessário;
3. Verifique os componentes eletrônicos internos da fonte de alimentação e substitua-os imediatamente se estiverem danificados.
3、 Falha de alta temperatura
Durante o uso da fonte de alimentação de alta frequência de oxidação, falhas de alta temperatura podem ocorrer devido a fatores como vibração da máquina e temperatura ambiente. Neste ponto, a fonte de alimentação precisa parar de funcionar automaticamente para proteger os componentes eletrônicos internos contra danos. Para solucionar tais falhas, as seguintes etapas podem ser tomadas:
1. Verifique se o ambiente ao redor da fonte de alimentação atende aos requisitos. Se for necessária a substituição, ela deve ser feita imediatamente;
2. Verifique a limpeza do dissipador de calor interno da fonte de alimentação. Se for necessária a limpeza, o dissipador de calor precisa ser limpo;
3. Verifique se os parâmetros de processo da fonte de alimentação estão corretos. Se forem necessárias alterações, elas precisam ser redefinidas.
Em suma, fontes de alimentação de alta frequência de oxidação podem encontrar vários defeitos durante o uso. Portanto, ao usar uma fonte de alimentação, é necessário ter um certo entendimento de várias falhas para solucionar e resolver problemas prontamente
Qual é o avanço do retificador de anodização IGBT?
1. Melhore a eficiência da conversão de energia
A tecnologia de energia de alta frequência pode melhorar a eficiência de conversão de fontes de alimentação porque a velocidade de comutação de correntes de alta frequência é mais rápida, o que pode converter eletricidade CA em eletricidade CC mais rapidamente e reduzir a perda de energia.
2. Reduza a perda de energia
A tecnologia de energia de alta frequência pode reduzir perdas de energia porque o período alternado da corrente de alta frequência é mais curto, o que pode concluir a transformação de energia, retificação, filtragem e outros processamentos mais rapidamente, reduzindo assim a perda de energia do fornecimento de energia.
3. Reduza o tamanho da fonte de alimentação
A tecnologia de energia de alta frequência pode reduzir o tamanho dos módulos de energia porque as correntes de alta frequência têm frequências mais altas e exigem componentes menores, permitindo que mais componentes sejam colocados no mesmo espaço e obtendo projetos de módulos de energia menores.
A diferença entre fonte de alimentação de alta frequência (retificador IGBT) e fonte de alimentação de tiristor (retificador SCR)
1、 Visão geral e características da fonte de alimentação de alta frequência
Fonte de alimentação de alta frequência é um tipo de fonte de alimentação com uma frequência relativamente alta, normalmente operando acima de 20 kHz. Uma fonte de alimentação de alta frequência consiste em um transformador de alta frequência e um capacitor, que pode gerar energia de alta tensão por meio de oscilação de alta frequência. Comparadas às fontes de alimentação de tiristores, as fontes de alimentação de alta frequência têm as seguintes características:
1. Alta eficiência:Fontes de alimentação de alta frequência transmitem quase nenhuma perda de energia, o que as torna mais eficientes do que fontes de alimentação de tiristores.
2. Tamanho pequeno:Devido à alta frequência operacional das fontes de alimentação de alta frequência, seus componentes podem ser menores, e o volume total da fonte de alimentação é menor do que o das fontes de alimentação de tiristores.
3. Ampla gama:Fontes de alimentação de alta frequência são adequadas para diversas ocasiões, como linhas de produção, laboratórios, medicina e outros campos.
2、 Visão geral e características da fonte de alimentação de silício controlável
Uma fonte de alimentação tiristorizada é um tipo de fonte de alimentação que usa dispositivos tiristorizados para controle. Seu princípio é controlar a potência de saída da fonte de alimentação alterando o tempo de condução dos dispositivos tiristorizados. Comparadas com fontes de alimentação de alta frequência, as fontes de alimentação tiristorizadas têm as seguintes características:
1. Alto consumo de energia:No processo de transmissão de energia elétrica através da fonte de alimentação do tiristor, haverá certa perda de energia, o que consome mais energia do que a fonte de alimentação de alta frequência.
2. Boa estabilidade:Devido ao uso de dispositivos tiristores para controlar a potência de saída das fontes de alimentação tiristores, sua estabilidade de tensão de saída é relativamente boa.
3. Cenários de aplicação restritos:Fontes de alimentação de silício controláveis são geralmente usadas em áreas como aviação e ferrovias, que exigem alta fonte de alimentação e têm uma faixa de aplicação estreita.
3、 Comparação entre fonte de alimentação de alta frequência e fonte de alimentação de silício controlável
1. Cenários de aplicação:Fontes de alimentação de alta frequência são adequadas para diversas ocasiões e podem ter uma faixa de entrada mais ampla, enquanto os cenários de aplicação de fontes de alimentação de tiristores são relativamente estreitos.
2. Índice de eficiência energética:Atualmente, a taxa de eficiência energética da maioria das fontes de alimentação de alta frequência é maior do que a das fontes de alimentação de tiristores, por isso as fontes de alimentação de alta frequência são mais populares em algumas ocasiões com altos requisitos de energia.
3. Estabilidade:Devido à boa estabilidade da tensão de saída das fontes de alimentação tiristorizadas, elas são mais adequadas para aplicações ou campos que exigem alta estabilidade do fornecimento de energia.
Fontes de alimentação de alta frequência e fontes de alimentação de tiristores têm suas próprias características, e o tipo de fonte de alimentação apropriado deve ser selecionado de acordo com as necessidades específicas.